
Oxalic acid (H₂C₂O₄), a naturally occurring organic compound, intrigues scientists, industrialists, and health enthusiasts with its unique properties and wide-ranging applications. Its versatility has established it as a key component across multiple industries.
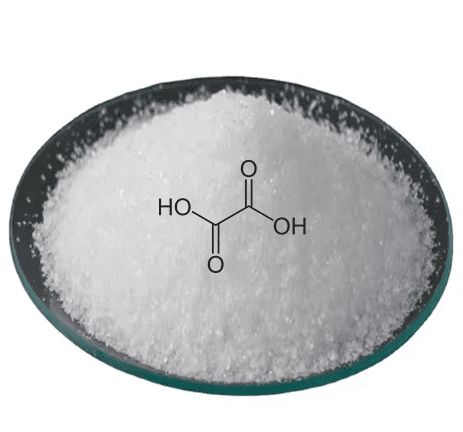
Chemical Properties and Structure
As a diprotic acid, oxalic acid can donate two protons in solution. Comprising two carboxylic acid groups connected by a carbon-carbon single bond, it forms a reactive molecular structure. In its pure state, it appears as a white, crystalline solid highly soluble in water, enabling ready dissociation and contributing to its acidic nature. These chemical properties underpin its industrial uses.
Natural Occurrence
Oxalic acid is abundant in nature, found in spinach, rhubarb, and cocoa. In plants, it forms insoluble calcium oxalate crystals as a defense against herbivores. It’s also produced by certain fungi and bacteria. While its natural presence is notable, industrial value lies in its extraction and refinement.
Industrial Applications
Oxalic acid plays indispensable roles in various industries:
Metalworking Industry
In metalworking, oxalic acid excels as a rust remover and cleaner. Industry data shows 70% of metal restoration projects use oxalic acid solutions. Its ability to chelate iron ions dissolves rust efficiently. For example, it can restore antique iron gates and machinery, saving time and reducing reliance on mechanical abrasion. Compared to other rust removers, it preserves metal integrity.
Textile Industry
The textile industry uses oxalic acid in dyeing and bleaching. It adjusts dye bath pH, ensuring even dye penetration and strong bonding, which improves colorfastness and brightness. Fabrics treated with oxalic acid resist fading better, giving high-end brands a market advantage.
Pharmaceutical Industry
In pharmaceuticals, oxalic acid serves as a key reagent in chemical synthesis for medications and APIs. Its precise reactivity helps chemists create complex molecular structures accurately. In antibiotic synthesis, it aids in forming essential chemical bonds, ensuring product effectiveness and purity.
Other Industries
Oxalic acid also applies in leather tanning and finishing, enhancing leather texture and durability. In woodworking, it bleaches and restores wooden surfaces, removing stains.
Health Considerations
Despite its industrial benefits, oxalic acid has health risks. Excessive consumption of oxalate-rich foods can lead to kidney stones, as oxalate binds with calcium in urine to form crystals. However, a balanced diet usually avoids excessive intake, and proper hydration helps prevent stone formation.
Safety Precautions
Handling oxalic acid in industry requires strict safety measures. As a strong acid, it causes severe skin and eye irritation. Workers must wear gloves, goggles, and protective suits. In case of contact, immediate rinsing with water for 15 minutes and medical attention are necessary. Proper storage away from incompatible substances ensures stability.
In conclusion, oxalic acid’s industrial applications highlight its value. From metal restoration to pharmaceutical synthesis, it drives industrial innovation. Continued exploration of its uses will further expand its impact on industries and daily life.
